Step 9 - Silence
Era summary
Era Overview
Event Summary
- The Changing Guard : Jerusalem is still ruled by Persia, then Greece, Then Rome
- Political Sect : Rebellious Jews try to free Judea from foreign rule
- Religious Sect : Two religious parties rise up in this time
- Messianic Hope : Expectations of a Messiah / Saviour grow
Event Details
The Changing Guard
The big changes in power:
- At the close of the Old Testament, Jerusalem is ruled by Persia. Aramaic is the common trading language
- Alexander the Great defeats the Persians in 333 B.C. and establishes Greek culture and the Greek language as a unifying force for that part of the world.
- When Alexander dies, his kingdom is quartered, but Hellenistic (Greek) culture is still advanced and remains the dominant influence.
- When Rome conquers that part of the world, Roman influences are introduced but for now the Greek influence is still strong.
Languages:
- In Judea the learned Jews spoke Hebrew, especially for scripture readings,
- The common Jews spoke Aramaic, the common language left overt from Persia,
- The educated (Hellenised) Jews spoke Greek ( like poeple world wide recently spoke French as a language of diplomacy)- the language of culture and philosophy and learning
- For all things governmental, political and military – Latin ( the language of Rome) was spoken).
Political Sect
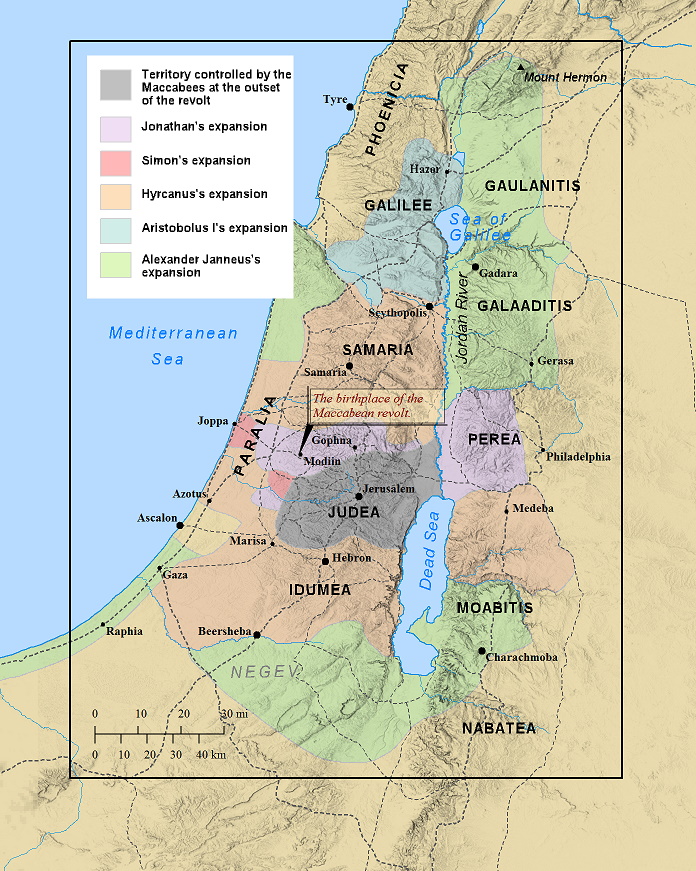
Through out the four hundred silent years (between the Old and New Testaments) militant Jews attempted to revolt against foreign rule and make Jerusalem and Judea free.
The most famous of these were called the Maccabees and the Zealots ( One of the disciples, Simon was a zealot – but not Simon Peter)
Religious Sect
There are two primary religious “parties” in Jerusalem during this time. Unfortunately, neither offers much guidance in true spirituality, as they are caught up in promoting a religious “legalism” of external adherence to rules while overlooking inner motivations and attitudes.
The Pharisees are orthodox and conservative, and they foster separation between themselves and “secular” society.
The Sadducees are more liberal. They are the party of the Jerusalem aristocracy, and they use their wealth and influence to keep the political waters calm.
A ruling board, called the Sanhedrin, is made up of representatives from both the Pharisees and Sadducees, but the two groups have little in common except their desire for religious freedom and, later, their antagonism for Jesus of Nazareth.
Messianic Hope
The “Messiah,” or “Savior,” is one who is prophesied throughout the Old Testament to come save the Jews.
Some feel they need spiritual salvation, and others are looking only for political salvation. For both reasons, the expectation and hope for the coming of the Messiah is strong during the four hundred Silent Years.
Events of the Silence Era seem to especially prepare the world for the coming of the Messiah:
- (1) This part of the world has a common language and a common culture, which facilitates the spread of a Messianic message.
- (2) The Roman Empire has brought this region military peace, an extensive system of roads and sea travel, and a common government so that people can travel extensively without interference.
- (3) The Jews are suffering such religious persecution and political humiliation that widespread hope and expectation of a savior exists.
These facts make the coming of Jesus of Nazareth, claiming to be the Messiah, an event that captures the attention of the entire Jewish world.
Extra Notes
A time line of important events:
Previously:
Assyrians -> Babylonians – >Medes -> Persians
( Nebuchadnezzar – >Belshazzar the Chaldean (Babylonian) king – > Darius the Mede – Cyrus the Persian)
(TIME LINE – from Agape Bible Study)
- -356BC Birth of Alexander son of Philip of Macedonia (Greek)
- -336BC Alexander the Great begins world conquest (Greek)
- -333BC conquers Syria (Currently ruled by the Persian Empire)
- -332BC conquest includes Judah, Tyre, and Gaza’entry into Egypt
- -331BC ends Persian empire by his victory at Arbela
- -330-326 BC conquest of Eastern satrapies and India
- -323BC Alexander dies and his kingdom is divided into 4 parts among his top generals. Judah will be ruled and fought over by 2 Greek dynasties:
- -Ptolemy I Soter becomes Pharaoh of Egypt & founds the Ptolemy dynasty
- -Seleucus I Nicator founds the Seleucus dynasty which stretched from modern Syria to the Indus River in India
- -250BC translation of Sacred Scriptures into the Greek language known as the Septuagint
- -175BC Seleucuid king Antiochus IV (175-163) decides to impose Greek culture on the Jews and to destroy the Jewish religion and culture.
- -175-170BC Onias III last legitimate high priest of the line of Zadok is assassinated. Qumran community [Dead Sea Scrolls] established in opposition to illegitimate priesthood in Jerusalem
- 168BC Antiochus IV has a pig sacrificed on the altar at the Temple and erects an altar & statue of the Greek god Zeus = the “abomination of desolation” in the Temple prophesized by Daniel.
- -166 Maccabean Revolt begins
- -165 Purification and rededication of the Temple
- -134-67 Hasmonean dynasty = established by John Hyrcanus descendant of the priest Mattathias. Hasmons were Priest-Kings of Judah
- -100BC birth of Julius Caesar
- -67-63 Civil war between sons of Alexander Jannaeus
- -63 Roman consul, Pompey, attacked and took possession of Jerusalem. He ended the Hasmonean monarchy made Judea a part of the Roman province of Syria. Hasmonean king Hyrcanus II is made high priest with the title of ethnarch and an Idumean named Antipater is appointed procurator by the Romans.
- -46 Cleopatra of Egypt gives birth of Caesar’s only son.
- -44BC Julius Caesar murdered. Marc Antony and Caesar’s great-nephew Octavian share power
- -43 Antony and Cleopatra VII of Egypt become lovers
- -42 birth of Tiberius [future emperor, step son of Octavian/Augustus Caesar]
- -40BC Herod, son of the Idumean Antipater and Cypris, an Arabian princess, becomes the Roman appointed King of Judea with the help of his friend Marc Antony. (Idumea is Edom the land of Jacob’s brother Esau)
- -37 Herod, King of Judea. After 3 years of fighting, Herod defeats the last Hasmonean heir and installs himself as king, marrying the Hasmonean princess Mariamme. He will murder 2 brothers-in-law, his wife, his mother-in-law, his brother and 3 of his sons before his death (and those are only family members’untold others also) in ? 4BC or 1BC. Since Herod observed Jewish dietary restrictions Augustus Caesar was quoted as saying “it is better to be Herod’s pig than Herod’s son.
- -31BC Antony and Cleopatera are defeated at Battle of Actium. Octavian is the victor.
- -30BC Octavian [great-nephew of Julius Caesar] becomes Caesar Augustus (title given in 27), Emperor of the Romans. It is the end of the Roman Republic and the birth of the Roman Empire
Readings for Biblical Period THE REVOLT OF THE MACCABEES AND THE RULE OF THE HASMONS
| The Rule of the Greek Seleucid Kings | Daniel 8:1-27; 1 Maccabees 1:10-24 |
| Mattathias Unleashes the Holy War | 1 Maccabees 2:1-7, 15-28 |
| Judah “The Hammer” | 1 Maccabees 2:49-50, 65-70; 3:1 |
| Purification of the Temple | 1 Maccabees 4:36-61 |
| The Alliance with Rome | 1 Maccabees 8:1-32 |
| The Death of Judah “The Hammer” | 1 Maccabees 9:14-22 |
| Jonathan Takes Command | 1 Maccabees 9:28-31, 37-66 |
| Judah caught between Egyptian and
Syrian Empires |
1 Maccabees 11:1-19 |
| The Death of Jonathan | 1 Maccabees 12:39-53; 13: 25-30 |
| Simon, High Priest and Ethnarch | 1 Maccabees 13:31-42 |
| John Hycanus – Independence | 1 Maccabees 16:1-24 |
